When cloud hard-sell ends and value-generation begins
The past few years have seen cloud adoption across enterprises increase manifold. With Global Organizations planning to choose cloud infrastructure as the top investment priority , cloud has officially become a way of life across enterprises. This adoption spans Infrastructure and Software-as-a-service models that leading software vendors such as Salesforce , Oracle & Service. This blog focuses on one methodology of leveraging the automation benefits in cloud, to ensure compliance to an Enterprise Cloud Governance model.
Great going thus far for the cloud story! However, it is time for a word of caution!
With such rapid growth comes hard-sell and hype. Enterprises need to realize the distinction between the old world and the new, and ensure they understand the impact.
With the great advantages of pay-per-use, no fixed fee, no contracts etc come the new paradigms of shared hardware, shared responsibilities and such. The burden shifts to the Enterprise , in ensuring that Governance, security and Business continuity require shared roles and responsibilities. This is a good change, offers the Enterprise more control, however it needs to be understood and implemented right.
So, how to safely harness the power of the cloud, and maximize the benefit .
The post-migration challenges
Once the initial cloud adoption drive sets in, Enterprises typically wake up to the following challenges
- Disparate proliferation and VMs and cloud assets across business solutions, departments
- Inadequate control, and management of cloud-cost owing to rapid growth
- Security and compliance oversight due to decentralized cloud deployments
- Shadow processes and footprints that evolve
These reasons, along with demand for stringent Compliance practices across Geos and Verticals, necessitate enterprises to have a thorough relook at the governance model of the cloud data centre. Thus arises the need for holistic cloud governance that sets policies and standards to controls Operations, Security and Costs.
It is thus imperative to have a well thought out and standardized cloud governance in place (ideally as a part of Initial cloud blueprint) that aims at achieving some key tenets.
Key tenets of cloud governance
- Cloud governance guided by industry-specific compliance policies and standards
- Enterprise security practices across multi-cloud deployments
- Seamless service integration and operations
- Financial cost control and proactive cost management
While enterprises need to encourage and accelerate cloud adoption , the above tenets need to be addressed and enforced in parallel.
Path towards setting up enterprise cloud governance
Gartner advocates the following steps to formalize Enterprise Cloud Governance:
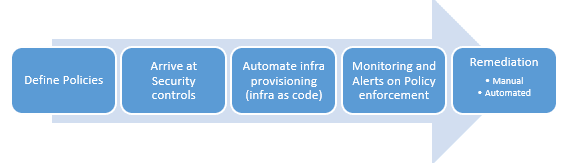
It starts with setting up a core group for governance that will have right mix of stakeholders with various representations. The core group the goes on to define governance blueprint and decide Implementation plan.
At the heart of cloud governance is arriving at the Policies. All cloud platforms come with clear Global compliance certifications. They must be factored into as well and further policies need to be chartered based on geographic, industry, platform, application and user specific guidelines. The policies would driven by following concerns
- Government and Industry bodies
- Enterprise Security operations(Sec Ops)
- By Network, Infrastructure Administrators (Infra Ops)
- Developers and Deployment teams (Dev Ops)
- End users
It is the next step that makes cloud governance all the more effective. Because it is not just about defining policies but ensuring policy adherence holds the key for cloud implementations. o Manual process here would be cumbersome and would lead to extreme unproductivity leading to an anti-thesis of cloud drive.
It is in this perspective, Infra-as-code deployment of cloud services as well as automated monitoring & remediation proves to be a significant solution. Cloud platforms provide complete spectrum of services that can be automated from definition to deployment and control. Hence, policies can be clearly defined with Security controls and can be automated for definitions and deployment of cloud resources. Once implemented the policies can be monitored for compliance and alerts can be triggered automatically on policy breaches. The policy breaches can also be remediated through automation. This eliminates complex manual processes or workflow systems that are needed for governance driven cloud setup.
An illustrative example of enterprise cloud governance
Let us look at an interesting case of Cloud Governance Automation to illustrate this further. A financial services provider, with a multi-cloud environment, as part of its security and compliance requirement, wants to setup automated security controls and policy remediations for its cloud deployments.
The Security controls are defined using ISO & PCI standards and as many as 200+ Security controls are defined to meet the control objectives.
The key challenge in this scenario is the need to cater to multi-cloud deployments. This requires mapping the security controls and translating the requirements for cloud platforms accordingly. While there will be cloud specific implementations, the key here is to identify common patterns that can be cloud agnostic. Why do we need this.. Enter cloud agonistic infra as code platforms such as Terraform, Cloud Custodian. These platforms can help achieve both Security control as well as remediation automation via infra as code scripts that run cross platform so that we write once and deploy across clouds.
Once the cloud agnostic model is identified, one way to approach the implementation would be by grouping the required services for automation and monitoring into clusters. The following is a sample cluster model by which cloud resources can be automated for deployment
- Cluster 0: Account and Subscription Services
- Cluster 1: Networking and Common Infrastructure services
- Cluster 2: Security Alerts, integration services
- Cluster 3: Application-specific cloud resources …and so on
This allows clusterwise management and deployment of security controls as well as helps in organized deployment of resources.
Post deployment the cloud resources would be monitored and managed via cloud management platforms like Arcus. Remediation scripts would be triggered on Policy violations that would help take the appropriate temporary as well as corrective actions.
Thus automated deployment, monitoring and remediation of cloud resources makes cloud governance a rewarding exercise by eliminating risks, compliance overlooks as well as by having a highly standardized process across the enterprise. By leveraging cross platform solutions, the automation would be easy to maintain and re-usable.



